High Frequency Checks: a template for data quality monitoring
HFC.RmdSupervising the quality of data collection is not straightforward. Survey questionnaires are often quite long and have systematic control is worth automatizing.
HighFrequencyCheck can be used to detect programming errors, surveyor errors, data fabrication, poorly understood questions, and other issues. The results of these checks can also be useful in improving your survey, identifying enumerator effects, and assessing the reliability of your outcome measures. It allows teams to catch survey issues and collection mistakes in time to correct them and ensure high-quality data
The HighFrequencyCheck package is a translation in in R of the Stata package based on best practices from Innovations for Poverty Action. High Frequency Checks are also recommend by the World Bank. It can be installed from github with devtools::install_github("unhcr/HighFrequencyChecks").
The package brings a series of convenience functions to monitor data quality during the data collection when running a survey with KoboToolbox (or any xlsform compatible platform).
Those are the basis of a feedback mechanism with enumerators and can be performed periodically during the data collection process to check for possible errors and provide meaningful inputs to the enumerators. All these functions do not have to be ran at the same period of time. They are provided there to help data supervisor to build reports:
A
wrapperfunction is included to generate directly an final data quality assessment Rmd ReportA
ShinyAppInterface is also included to provide a live monitoring dashboard to be run locally.
Introduction
Measuring data collection quality
Data collection quality monitoring includes 4 different dimensions
- Correct set-up of data collection devices
- Data collected according the sampling plan
- Enumerator rigorous work standards
- Enumerator productivity
Ideally the data collection monitoring dashboard should be known to all enumerators so that they are aware of the data quality metrics that will be used to assess the quality of their work and potentially some incentive can be offered for the enumerators performing on the quality metrics (It is good to recall that each records in household survey cost between 15 to 50 USD). Some of those indicators can support some remedial supervision interventions, such as calling individually the enumerator and point some specific issues that were detected.
It is important to prepare high frequency checks (code and instructions), as part of the data quality assurance plan, before before starting with field data collection.
Below are the required configuration and an illustration of those indicators based on a demo dataset included in the package.
Specific variables to be controlled
When it comes to back checks, variables can be divided into the following different categories:
Type 1 variables are based on straightforward questions where there is very little possibility of error. For example, age and education. If there is an error in these variables, it means there is a serious problem with enumerator, or with the questions.
Type 2 variables are based on questions where a risk of error is possible. For example, questions based on sensitive topics, or questions that involve calculations. If there is an error in these variables, there might be a need to provide further training for enumerators.
Type 3 variables are based on questions about the survey instrument, and errors in this case provide feedback which can help improve the survey instrument itself. This is often the case for questions including or other, please specify question type.
Process configuration
Loading survey dataset (microdata)
In a production environment, it is possible to connect this a live API (kobotoolbox, ODK , etc.)
ds <- HighFrequencyChecks::sample_dataset
Configuring dates variable…
dates <- c("survey_start","end_survey") surveyDate <- "survey_date" ## Official date for start of data collection startDataCollection <- "11/11/2018" dateFormat <- "%m/%d/%Y" # start_collection <- "2020-10-05" # What is the minimum survey duration in minutes (when using all skip logic)? minimumSurveyDuration <- 30 minimumSurveyDurationByIndividual <- 10 # Standard value # sdval <- 2 ## Related actions... deleteIsInterviewCompleted <- FALSE deleteIsSurveyOnMoreThanADay <- FALSE deleteIsSurveyEndBeforeItStarts <- FALSE deleteIsSurveyStartedBeforeTheAssessment <- FALSE deleteIsSurveyMadeInTheFuture <- FALSE deleteIsInterviewTooShort <- FALSE deleteIsInterviewTooShortForTheHouseholdSize <- FALSE
Configuring unique ID…
uniqueID <- "X_uuid" ## Related actions deleteIsUniqueIDMissing <- FALSE deleteIsUniqueIDDuplicated <- FALSE
Configuring Enumerator
# Variable used to record enumerator identifiers enumeratorID <- "enumerator_id" ## Related action enumeratorcheck <- TRUE
Configuring Consent
# Variable recording initial consent surveyConsent <- "survey_consent" ## Related action deleteIsInterviewWithConsent <- FALSE
Configuring numeric questions
## Check on numeric variables #### questionsSurveySmallValues <-c(consent_received.food_security.spend_food=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_medication=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_education=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_fix_shelter=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_clothing=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_hygiene=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_fuel=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_hh_items=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_transport=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_communication=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_tobacco=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_rent=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_debts=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_other=25000) questionsSurveyBigValues <-c(consent_received.food_security.spend_food=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_medication=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_education=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_fix_shelter=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_clothing=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_hygiene=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_fuel=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_hh_items=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_transport=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_communication=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_tobacco=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_rent=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_debts=25000, consent_received.food_security.spend_other=25000)
Configuring categoric questions
otherPattern <- "_other$" # Variable recording multiples screening questions questionsEnumeratorIsLazy <- c(consent_received.shelter_nfi.non_food_items=3, consent_received.food_security.main_income=3, consent_received.child_protection.boy_risk=3, consent_received.child_protection.girl_risk=3)
Configuring sampling plan
The sampling plan is defined through the sampling strategy. It includes for each enumerator the sufficient details for the enumerator to reach out to respondent satisfying the sampling target definition (i.e. name, location, phone number)
sampleSizeTable <- HighFrequencyChecks::SampleSize # correction for uppercase/lowercase in the site name sampleSizeTable$Union <- tolower(sampleSizeTable$Union) # name as a string of the field in the sampling frame where the site is stored sampleSizeTableSite ="Union" # name as a string of the field in the dataset where the site is stored dsSite <- "union_name" # name as a string of the field where the number of points # generated is stored in the sampling frame sampleSizeTableAvailable ="TotPts" # name as a string of the field in the sampling frame where the site is stored sampleSizeTableTarget ="SS"
Configuring geodata for the surveyed area
Often sampling strategy includes a geographic coverage.
#This can be overview through either: ## a defined polygon, aka area or admin unit adminBoundaries <- HighFrequencyChecks::admin # correction for uppercase/lowercase in the site name ds$union_name <- tolower(ds$union_name) # Unique key with the survey dataset is changed # to all small cap for further join adminBoundaries$Union <- tolower(adminBoundaries$Union) # OR a sampling point, around which enumerators are supposed to randomly interview persons. sampledPoints <- HighFrequencyChecks::SamplePts # Name of variables for geographic coordinates as recorded by data collection device GPS dsCoordinates <- c("X_gps_reading_longitude","X_gps_reading_latitude") # Name of location (__matching external geodata__) dsSite <- "union_name" #Name of unique key in polygon file adminBoundariesSite <- "Union" #Size of the buffer in meters around the assigned data collection location points buffer <- 10 ## related cleaning actions deleteIsInterviewAtTheSamplePoint <- FALSE correctIsInterviewInTheCorrectSite <- FALSE
Report Configuration
# Variable to be checked # reportingcol <- c("enumerator_id","X_uuid") # formulas as a list of string used to compute the final number # of eligible surveys and the variance from the target # (C('formula1','formula2')). # the values/fields available are: done and the ones generated # according the survey consent values (one per value) # formul = c("done-no-not_eligible","done-no-not_eligible-SS") # column names as a list of string to order the colums in the result # the columns available are: site, done, final, variance and # the ones generated according the survey consent values (one per value) # colorder = c("site","SS","TotPts","done","not_eligible","no","yes","final","variance") consentForValidSurvey <- "yes"
Corrective actions
Correct set-up of data collection devices and encoding of the forms
These checks are designed to ensure that responses are consistent for a particular survey instrument, and that the responses fall within a particular range. For example, checks to ensure that all variables are standardized, and there are no outliers in the data. Share a daily log of such errors, and check if it is an issue with enumerators, in which case there might be a need to re-train enumerators.
Missing data: Are some questions skipped more than others? Are there questions that no respondents answered? This may indicate a programming error.
Categorical variables: Are respondents selecting the given categories or are many respondents selecting “None of the above”, or “other”? If conducting a survey, you may want to add categories or modify your existing ones.
Too many similar responses: Is there a question where all respondents answer in the same way?
Respondent ID
Respondent IDs: Are there duplicates of your unique identifiers? If so, does the reason why make sense? (e.g., one circumstance in which there may be duplicates of unique IDs is when surveyors have to end and restart an interview.) Are there blank or invalid IDs? This might be a sign your surveyors are not interviewing the correct respondent.
list_unique_id <- HighFrequencyChecks::isUniqueIDDuplicated(ds, uniqueID, surveyConsent) ds <- list_unique_id[[1]] if(nrow(list_unique_id[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_unique_id[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors: Duplicate respondent ID") } else { cat(">__No errors__: All records have a unique repondent ID") }
list_missing_id <- HighFrequencyChecks::isUniqueIDMissing(ds, uniqueID, surveyConsent) ds <- list_missing_id[[1]] if(nrow(list_missing_id[[2]] ) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_missing_id[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors: Missing respondent ID") } else { cat(">__No errors__: All records have an ID") }
Configuration of dates on device
- Checking record for which interview that do not end on the same day as they started
list_date_mistake <- HighFrequencyChecks::isSurveyOnMoreThanADay(ds, surveyConsent, dates) ds <- list_date_mistake[[1]] if(nrow(list_date_mistake[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_date_mistake[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors") } else { cat(">__No errors__: All interviews ended on the same day as they started") }
No errors: All interviews ended on the same day as they started
- Checking record for which interview ended before they start
list_date_mistake2 <- HighFrequencyChecks::isSurveyEndBeforeItStarts(ds, surveyConsent, dates) #ds <- list_date_mistake2[[1]] if(nrow(list_date_mistake2[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_date_mistake2[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors: interviews ended before they start") } else { cat(">__No errors__: All interviews ended before they start") }
No errors: All interviews ended before they start
- Checking record for which interview tagged in the future
list_date_mistake3 <- HighFrequencyChecks::isSurveyMadeInTheFuture(ds, surveyConsent, dates) #ds <- list_date_mistake3[[1]] if(nrow(list_date_mistake3[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_date_mistake3[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors - date are not in the future") } else { cat(">__No errors__: records date are not in the future") }
No errors: records date are not in the future
Data collected according the plan
Completed interviews
list_dateInterviewCompleted <- HighFrequencyChecks::isInterviewCompleted(ds, surveyConsent, dates) ds <- list_dateInterviewCompleted[[1]] if(nrow(list_dateInterviewCompleted[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_dateInterviewCompleted[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors - records withtout end date") } else { cat(paste0(">__No errors__: all records have an end date ")) }
No errors: all records have an end date
Interviews made before the first day of data collection
list_date_mistake4 <- HighFrequencyChecks::isSurveyStartedBeforeTheAssessment(ds, dates, surveyConsent, startDataCollection) ds <- list_date_mistake4[[1]] if(nrow(list_date_mistake4[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_date_mistake4[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors - records occured after the official beginning of data collection") } else { cat(paste0(">__No errors__: all records occured after the official beginning of data collection on ", startDataCollection)) }
No errors: all records occured after the official beginning of data collection on 11/11/2018
Enumerators who made a survey below 30 minutes
list_duration_Xmin <- HighFrequencyChecks::isInterviewTooShort(ds, surveyConsent, dates, minimumSurveyDuration) ds <- list_duration_Xmin[[1]] if(nrow(list_duration_Xmin[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_duration_Xmin[[2]], caption = paste0("Detected records with errors - Interviews duration shorter than ", minimumSurveyDuration)) } else { cat(paste0(">__No errors__: No interviews duration shorter than ", minimumSurveyDuration)) }
Recorded site name for each interview matches the name of the location
list_site <- HighFrequencyChecks::isInterviewInTheCorrectSite(ds, dsSite, dsCoordinates, adminBoundaries, adminBoundariesSite, surveyConsent) ds <- list_site[[1]] if(nrow(list_site[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_site[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors - location name not matching with GPS") } else { cat(">__No errors__: all records location name not matching with GPS") }
Recorded locations for each interview within a 10 meters buffer from a sample point
list_sitept <- HighFrequencyChecks::isInterviewAtTheSamplePoint(ds, dsCoordinates, sampledPoints, buffer, surveyConsent) ds <- list_sitept[[1]] if(nrow(list_sitept[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(list_sitept[[2]], caption = "Detected records with errors - recorded location too far from sampling points") } else { cat(">__No errors__: all records location in accpetable distance from sampling points") }
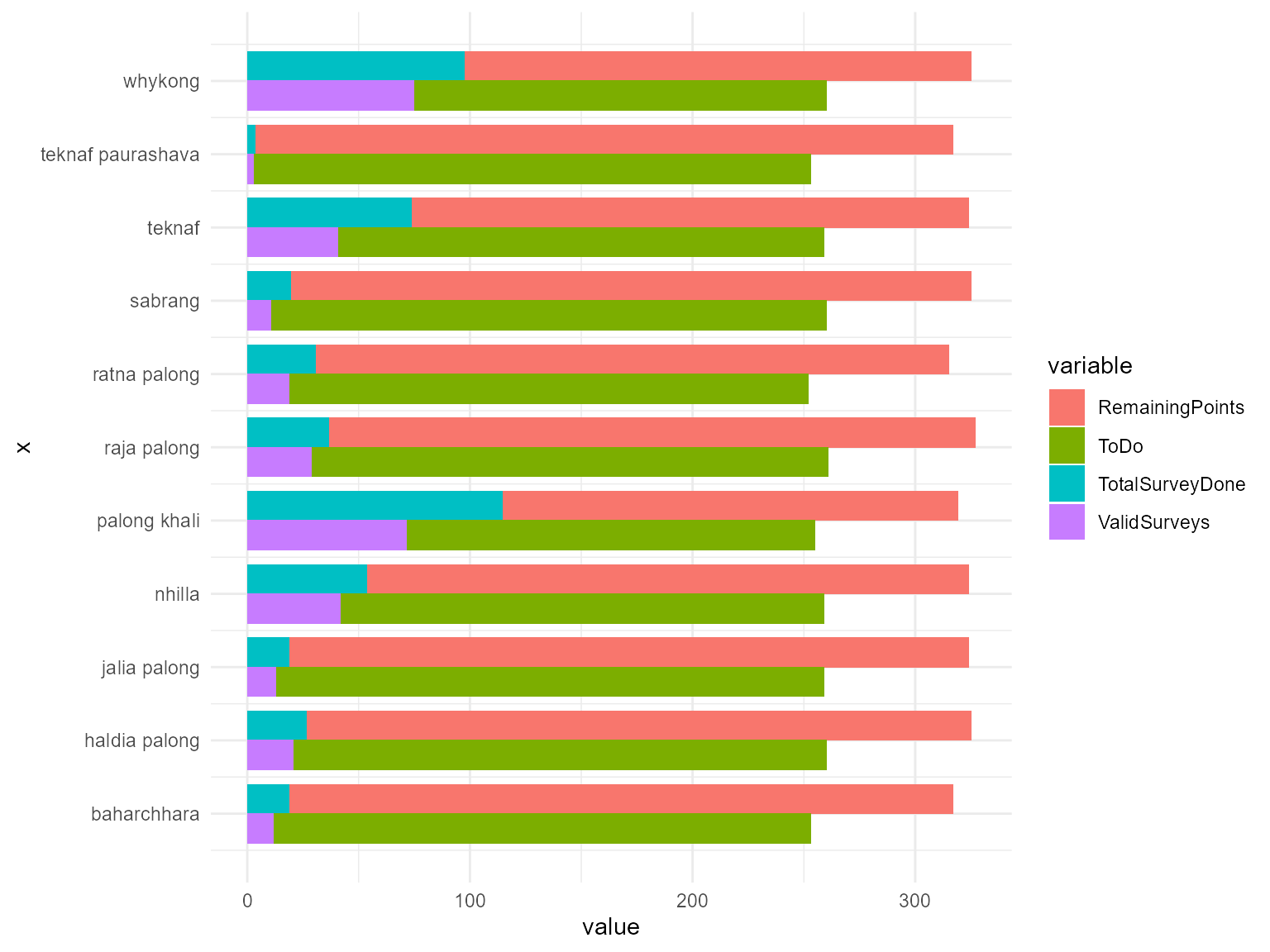
Tracking sheet per site
Test for target number: since surveys are submitted in daily waves, keep track of the numbers of surveys submitted and the target number of surveys needed for an area to be completed.
if(is.null(sampleSizeTable) | nrow(sampleSizeTable)==0 | !is.data.frame(sampleSizeTable)){ cat("You have not provided a sampling plan.") } else { trackingSheet <- HighFrequencyChecks::assessmentTrackingSheet(ds, dsSite, sampleSizeTable, sampleSizeTableSite, sampleSizeTableTarget, sampleSizeTableAvailable, surveyConsent, consentForValidSurvey) DT::datatable(trackingSheet[[2]], caption = "trackingSheet") }
if(is.null(sampleSizeTable) | nrow(sampleSizeTable)==0 | !is.data.frame(sampleSizeTable)){ cat("You have not provided a sampling plan.") } else { trackingSheet <- HighFrequencyChecks::assessmentTrackingSheet(ds, dsSite, sampleSizeTable, sampleSizeTableSite, sampleSizeTableTarget, sampleSizeTableAvailable, surveyConsent, consentForValidSurvey) print(trackingSheet[[4]]) }
Pro-active actions
Enumerators rigorous work standards
These are designed to check if data shared by any particular enumerator is significantly different from the data shared by other enumerators. Some parameters to check enumerator performance include percentage of “Don’t know” responses, or average interview duration. In the first case, there might be a need to re-draft the questions, while in the second case, there might be a need to re-train enumerators.
Durations of Interviews
Beware that Interviews with potential errors on the dates are not marked for deletion which can lead to weird duration
list_dur <- HighFrequencyChecks::assessmentDuration(ds, dates) # ds <- dts cat("> The total time of data collection is ", list_dur[[1]], " minutes and the average time per survey is ", list_dur[[2]], " minutes")
The total time of data collection is minutes and the average time per survey is minutes
Responses with outliers
Outliers can be observed when some respondents reporting values drastically higher or lower than the average response. This may require to have these variables to be top or bottom coded. Many outlier checks can be directly programmed into the survey, either to flag responses or bar responses that are outside the acceptable range.
log_outlier <- HighFrequencyChecks::surveyOutliers(ds, enumeratorID, enumeratorCheck=enumeratorcheck) if(nrow(as.data.frame(log_outlier[[2]])) > 0 ){ DT::datatable(log_outlier[[2]], caption = paste0("Detected records with errors - Answers with outliers")) }
Numeric value above a certain threshold
if(is.null(questionsSurveyBigValues) ){ cat("You have not indicated the numeric variables to look at") } else { reportlog_big <- HighFrequencyChecks::surveyBigValues(ds, questionsSurveyBigValues, enumeratorID, enumeratorCheck=enumeratorcheck) if(nrow(as.data.frame(reportlog_big[[2]])) > 0 ){ DT::datatable(reportlog_big[[2]], caption = paste0("Detected records with errors - Numeric values above threshold")) } }
Enumerators who pick up less than a predifined number of answers per specific questions:
DT::datatable(data.frame(minimumAnswers=questionsEnumeratorIsLazy))
reportlog_less_X_answers <- HighFrequencyChecks::enumeratorIsLazy(ds, enumeratorID, questionsEnumeratorIsLazy) if(nrow(as.data.frame(reportlog_less_X_answers[[2]])) > 0 ){ DT::datatable(reportlog_less_X_answers[[2]], caption = paste0("Detected records with errors - Enumerators who pick up less than a predifined number of answers per specific questions")) }
Number of other distinct values (for the questions with a possibility of other)
reportlog_others_values <- HighFrequencyChecks::surveyOtherValues(ds, otherPattern, enumeratorID, TRUE) if(nrow(reportlog_others_values[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(reportlog_others_values[[2]], caption = paste0("Detected of other distinct values")) }
Enumerator productivity
How many completed interview per day?
reportlog_productivity <- HighFrequencyChecks::assessmentProductivity(ds, surveyDate, dateFormat, surveyConsent) if(nrow(reportlog_productivity[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(reportlog_productivity[[2]], caption = paste0("Completed interview per day")) }
How many attempted interview per day and obtained consent?
reportlog_nb_status <- HighFrequencyChecks::assessmentDailyValidSurveys(ds, surveyDate, dateFormat, surveyConsent) if(nrow(reportlog_nb_status[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(reportlog_nb_status[[2]], caption = paste0("attempted interview per day and obtained consent")) }
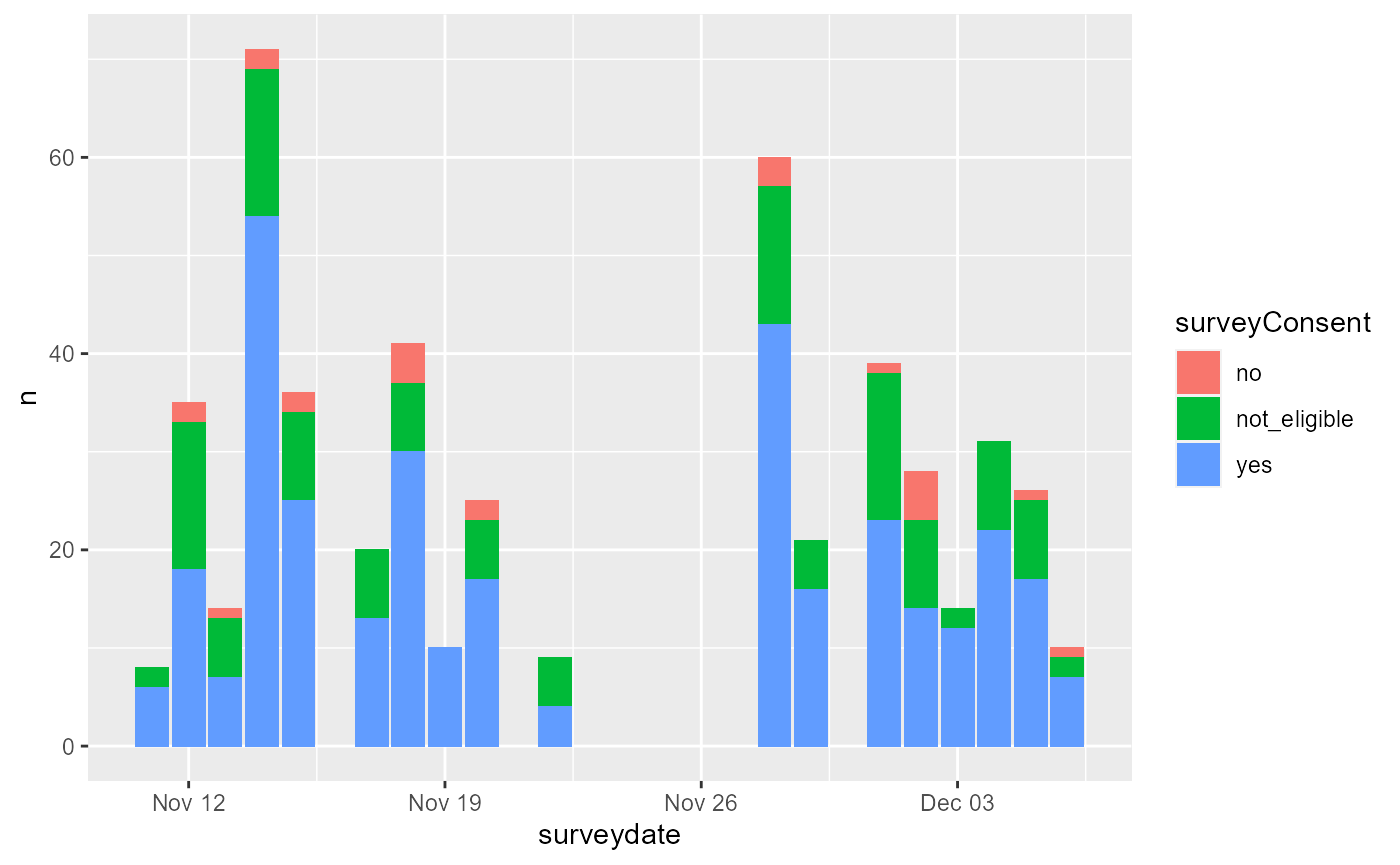
Percentage of survey per consent status by enumerator
reportlog_refusal <- HighFrequencyChecks::enumeratorSurveysConsent(ds, surveyConsent, enumeratorID) if(nrow(reportlog_refusal[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(reportlog_refusal[[2]], caption = paste0("Percentage of survey per consent status by enumerator")) }
Average interview duration by enumerator
reportlog_duration <- HighFrequencyChecks::enumeratorSurveysDuration(ds, dates, enumeratorID) if(nrow(reportlog_duration[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(reportlog_duration[[2]], caption = paste0("Average interview duration by enumerator")) }
Number of surveys per day by enumerator
reportlog_nb_survey <- HighFrequencyChecks::enumeratorProductivity(ds, surveyDate, enumeratorID) if(nrow(reportlog_nb_survey[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(reportlog_nb_survey[[2]], caption = paste0("Number of surveys per day by enumerator")) }
Enumerators with productivity significantly different from the average (low or high)
reportlog_productivity <- HighFrequencyChecks::enumeratorProductivityOutliers(ds, enumeratorID, surveyDate) if(nrow(reportlog_productivity[[2]]) > 0){ DT::datatable(reportlog_productivity[[2]], caption = paste0("Enumerators with productivity significantly different from the average")) }